Command Reference Guide
Commands must follow a PULSE-specific format, which may vary from DairyComp 305's command language and structure. Expand the sections below to learn more:
To run multiple commands simultaneously, use an exclamation point (!) to separate commands.
Command text is not case-sensitive.
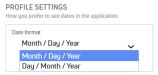
PULSE interprets the order of month and day based on your User Profile Date format setting.
The year may be two or four digits, and month and day may be one or two digits. Use a forward slash (/) or period (.) to separate year, month, and day. Dates may be specified in any of the following formats:
|
|
For instance, September 17, 2019, can be formatted as:
- 2019/09/17, 9.17.19, 9/17/19, or 9/17 if your date format is set to Month/Day/Year
- 2019/17/09, 17.9.19, 17/9/19, or 17/9 if your date format is set to Day/Month/Year
DC305![]() DairyComp 305 - VAS Dairy Management Software and PULSE accommodate date shortcuts to speed up the typing of commands. Date shortcuts may be used for any date items and work as follows:
DairyComp 305 - VAS Dairy Management Software and PULSE accommodate date shortcuts to speed up the typing of commands. Date shortcuts may be used for any date items and work as follows:
- The number is the date in the current month (if today
 Today's date or already occurred)
Today's date or already occurred) - The number is a date in the previous month (if not yet occurred)
For instance, if you enter MKDAT=3, and today is October 3, then the results show milk withdrawals ending today. If you enter FDAT>14 and today is October 1, the results include animals with fresh dates of September 15 through October 1.
Double quotes (") are required to identify a string in the command line. For instance, CODA="TEST".
The animal ID![]() Identifier is always included in LIST (SHOW) results, even if not specified in the command.
Identifier is always included in LIST (SHOW) results, even if not specified in the command.
Sort and condition keywords (BY, DOWNBY, FOR) must follow a prescribed order in LIST (SHOW) and SUM commands.
AND is implied between multiple conditional items. For instance, FORLACT>0 DCC>220 DDAT=2019/07/30 includes all results where the following is true: lactation number is greater than zero AND days carrying calf is less than 220 days AND due![]() Due to freshen date is July 30, 2019.
Due to freshen date is July 30, 2019.
Use a semicolon (;) to indicate OR. For instance, PEN=1;3;5 includes pens 1 OR 3 OR 5.
To use compound OR conditions, no semicolon (;) is required. Separate each condition with parenthesis (). For instance, FOR(LACT>0 DDAT=2019/07/30) (COD1>0 COD2=0) includes results where the following is true: lactation number is greater than zero and due date is July 30, 2019 OR COD1![]() Wildcard 1 byte item (0-255) is greater than zero and COD2
Wildcard 1 byte item (0-255) is greater than zero and COD2![]() Wildcard 2 byte item (0-32000) is equal to zero.
Wildcard 2 byte item (0-32000) is equal to zero.
Extra spaces between items are ignored.
In PULSE command line, any switches must immediately follow the command word. The following switches are currently supported in the specified command(s):
|
Switch |
Definition |
Command(s) |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| \B |
Includes results for both live and dead animals. Without the switch, command results include live animals only. |
|
LIST \B ID LACT DIM RPRO ARDAT FOR FDAT>-7 BY LACT Capture live and dead animal data for recently freshened animals by lactation. |
| \D |
Limits results to dead cows only. |
|
COUNT \D FOR LACT=1 ARDAT>-90 Capture total number of dead animals in their first lactation in the last 90 days. |
| \S |
Sets the standard deviation |
SUM |
SUM \S MILK PCTF PCTS LGSCC BY lact FOR LACT>0 Analyze sample standard deviation data for milk composition and quality by lactation. |
| \Z |
Includes zero values in averages and standard deviation calculations. Without the switch, average, standard deviation, mode |
SUM |
SUM \Z TKET BY LCTGP FOR FDAT>-365 Analyze the number of times ketosis |